The unique model of this tale seemed in Quanta Mag.
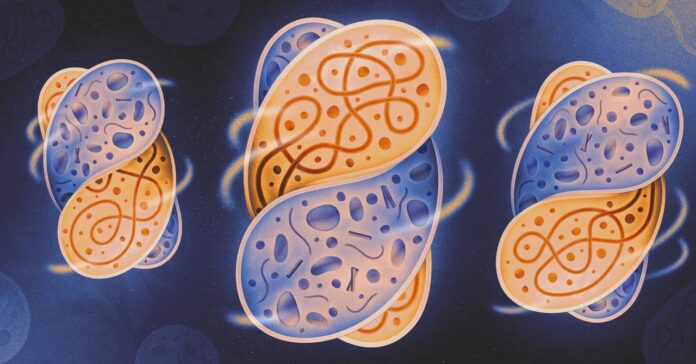
A long way from being solo operators, maximum single-celled microbes are in complicated relationships. Within the ocean, the soil, and your intestine, they could fight and devour each and every different, alternate DNA, compete for vitamins, or feed on one some other’s by-products. Now and again they get much more intimate: One cellular may slip within some other and make itself relaxed. If the prerequisites are good, it could keep and be welcomed, sparking a dating that would closing for generations—or billions of years. This phenomenon of 1 cellular dwelling within some other, known as endosymbiosis, has fueled the evolution of complicated existence.
Examples of endosymbiosis are all over the place. Mitochondria, the power factories for your cells, have been as soon as free-living micro organism. Photosynthetic crops owe their sun-spun sugars to the chloroplast, which used to be additionally in the beginning an impartial organism. Many bugs get crucial vitamins from micro organism that are living within them. And closing yr researchers came upon the “nitroplast,” an endosymbiont that is helping some algae procedure nitrogen.
Such a lot of existence depends on endosymbiotic relationships, however scientists have struggled to know the way they occur. How does an internalized cellular evade digestion? How does it discover ways to reproduce within its host? What makes a random merger of 2 impartial organisms right into a strong, lasting partnership?
Now, for the primary time, researchers have watched the hole choreography of this microscopic dance through inducing endosymbiosis within the lab. After injecting micro organism right into a fungus—a procedure that required inventive problem-solving (and a bicycle pump)—the researchers controlled to spark cooperation with out killing the micro organism or the host. Their observations be offering a glimpse into the prerequisites that make it imaginable for a similar factor to occur within the microbial wild.
The cells even adjusted to one another sooner than expected. “To me, which means that organisms need to in truth are living in combination, and symbiosis is the norm,” mentioned Vasilis Kokkoris, a mycologist who research the cellular biology of symbiosis at VU College in Amsterdam and wasn’t concerned within the new learn about. “In order that’s large, large information for me and for this international.”
Early makes an attempt that fell brief expose that the majority mobile amorous affairs are unsuccessful. However through figuring out how, why, and when organisms settle for endosymbionts, researchers can higher perceive key moments in evolution, and likewise doubtlessly increase artificial cells engineered with superpowered endosymbionts.
The Mobile Wall Leap forward
Julia Vorholt, a microbiologist on the Swiss Federal Institute of Generation Zurich in Switzerland, has lengthy confused over the instances of endosymbiosis. Researchers within the box theorized that after a bacterium sneaks into a number cellular, the connection teeters between an infection and unity. If the bacterium reproduces too temporarily, it dangers depleting the host’s assets and triggering an immune reaction, ensuing within the loss of life of the visitor, the host, or each. If it reproduces too slowly, it received’t identify itself within the cellular. Best in uncommon instances, they idea, does the bacterium reach a Goldilocks reproductive fee. Then, to develop into a real endosymbiont, it should infiltrate its host’s reproductive cycle to affix a trip to the following era. In spite of everything, the host’s genome should in the end mutate to house the bacterium—permitting the 2 to conform as a unit.
“They develop into addicted to one another,” Vorholt mentioned.




 #shorts #shortsfeed #nature #youtubeshorts #iciness
#shorts #shortsfeed #nature #youtubeshorts #iciness