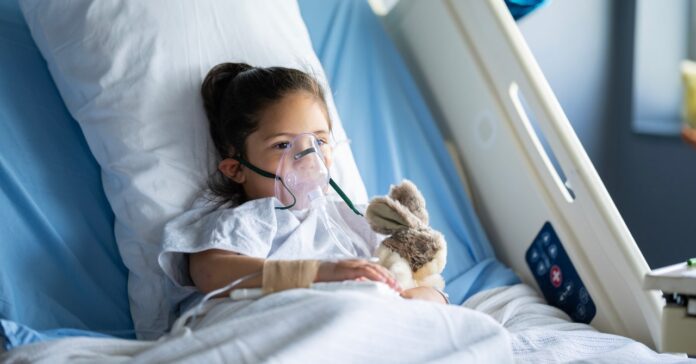
After 25 years as a pediatric infectious sicknesses specialist, Asunción Mejías is just too acquainted with the fatal unpredictability of breathing syncytial virus (RSV), an an infection that hospitalizes as much as 80,000 kids below the age of five annually in the United States.
“It’s a illness which is able to alternate in no time,” says Mejías, who works at St. Jude Youngsters’s Analysis Medical institution in Memphis, Tennessee. “I’ve all the time informed my colleagues that for each two kids which might be admitted, one can move to the ICU within the subsequent 3 hours and the opposite one would possibly move house tomorrow. It’s utterly unpredictable.”
RSV infections are quite common, to the purpose that just about each kid could have one earlier than they flip 2 years outdated. Most youngsters enjoy signs very similar to a chilly, like coughing and sneezing, however some can broaden critical lung illness: RSV is liable for greater than 100,000 toddler deaths globally annually, just about part of that are in small children below 6 months of age.
The issue is, with the exception of a couple of recognized threat components corresponding to untimely delivery and preexisting lung prerequisites, it’s onerous to inform which kids can be worst affected. “80 % of youngsters that finally end up within the medical institution with RSV appear utterly wholesome,” Mejías says. “They had been born complete time period, and don’t have any threat components for critical illness.”
So world wide, other analysis teams are making an attempt to coach system studying algorithms or broaden statistical fashions that may point out which kids are maximum at risk of RSV. In line with huge databases of digital well being data, those gear goal to spot teams of threat components that may lend a hand are expecting which kids are much more likely to be hospitalized with an an infection. Well being care suppliers can then use this knowledge to prioritize essentially the most at-risk kids for vaccines and different preventative measures.
Previous this 12 months, breathing epidemiologist Tina Hartert and her colleagues at Vanderbilt College evolved one such device the use of a statistical type to spot a suite of nineteen threat components for RSV, after coaching it on knowledge from greater than 400,000 babies at the Tennessee Medicaid program. “It lets in a person toddler’s threat to be calculated at delivery,” says Hartert.
Probably the most variables used within the device are unsurprising. Prenatal smoking, as an example, is understood to impair lung construction within the unborn fetus, making a toddler extra at risk of viral pneumonia, whilst small children with a low delivery weight already lack the power to respire typically. On the other hand, in lots of circumstances, Hartert says this can be a mixture of various threat components that converge to make a kid susceptible. “Assessing simply particular person components misses numerous at-risk babies,” she says.
In 2023, regulators in the United States authorized a vaccine referred to as Abrysvo this is designed to be given to moms all the way through weeks 32 to 36 of being pregnant, with the purpose of making sure that small children are born with protecting antibodies towards RSV. Additionally they authorized a drug referred to as Beyfortus, a laboratory-made protein referred to as a monoclonal antibody, which will also be administered via a unmarried injection to offer coverage forward of the iciness RSV season.




 #shorts #shortsfeed #nature #youtubeshorts #iciness
#shorts #shortsfeed #nature #youtubeshorts #iciness